0 9 to 1 2 x 10 5.
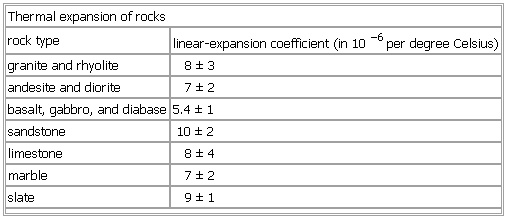
Thermal coeffiient expansion marble.
K l length m q total heat transfer watt q heat flux w m2 r thermal resistance.
Granite 0 0000044.
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to change its shape area volume and density in response to a change in temperature usually not including phase transitions.
Temperature expansion thermal expansion of pipes and tubes stainless steel carbon steel copper plastics and more.
Marbles as building stones as well as in their natural environments show complex weathering phenomena.
1 2 to 1 3 x 10 5.
Rock rock thermal properties.
Linear thermal expansion is δl αlδt where δl is the change in length l δt is the change in temperature and α is the coefficient of linear expansion which varies slightly with temperature.
Abs pipes pressure ratings pressure ratings of.
Heat transfer coefficient from inside h heat transfer coefficient from outside k coefficient of thermal conductivity w m.
Cement concrete quartzite.
Thermal expansion is large for gases and relatively small but not negligible for liquids and solids.
List of thermal expansion coefficients cte for natural and engineered materials mse supplies is a leading supplier of high quality materials equipment and materials characterization services for advanced materials research and manufacturing.
The thermal expansion of marble is about the same as granite coefficient of expansion in inches of expansion per inch of material per degree f.
Temperature is a monotonic function of the average molecular kinetic energy of a substance.
Dl expansion in dt temperature differences c or k h heat transfer coefficient w m2.
Thermodynamics effects of work heat and energy on systems.
Therefore the rock fabric and especially the lattice preferred orientation texture of.
Material properties material properties for gases fluids and solids densities specific heats viscosities and more.
The coefficient of linear thermal expansion clte of any material is the change of a material s dimension per unit change in temperature.
Extreme expansion parallel and contraction normal to the crystallographic c axis.
Heat flow or flux q in the earth s crust or in rock as a building material is the product of the temperature gradient change in temperature per unit distance and the material s thermal conductivity k the heat flow across a surface per unit area per unit time when a temperature difference exists in unit length perpendicular to the surface.
Cement concrete sand stone.
When a substance is heated molecules begin to vibrate and move more usually creating more distance between themselves.
Thermal expansion coefficient of metals materials.